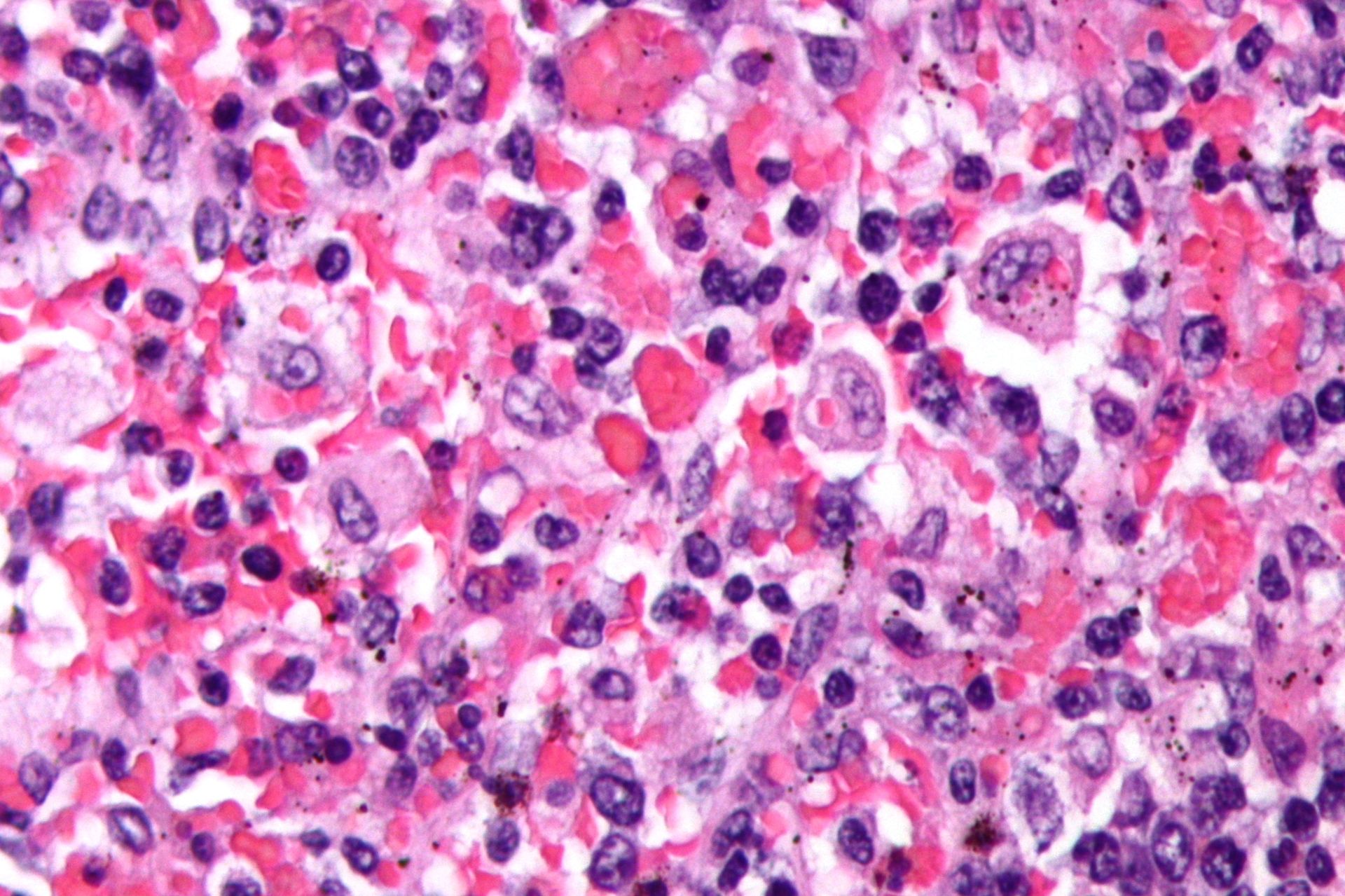
Fever of Unknown Origin and Giant Cell Arteritis

Teaching Points
- Definition of Fever of Unknown Origin (FUO):
- Fever for >3 weeks
- Documented T>38.3
- At least 1 week of inpatient investigation or 3 clinic visits
- FUO Differential: infection (24.5%), malignancy (14.5%), inflammatory (23.5%), micellaneous (7.5%)
- FUO labs: CBC, ESR/CRP, LFTs, Blood cultures, UA, CXR, PPD/quant gold, HIV, hepatitis serologies, ANA, RF